low end tidal co2 acidosis
It is the measurement of CO2 at the completion of exhalation and roughly correlates to the CO2 present in arterial blood. Only effective chest compressions can restore blood flow.

End Tidal Co2 Icu Nursing Medical Knowledge Respiratory Therapy
1 It can identify hypoventilation earlier than other monitoring tools we have at our disposal in the.

. The arterial CO2 value for normal breathing at rest is 40 mm. When a person suffers cardiac arrest there is no circulation metabolism or CO2 production. This may result from such ventilatory problems as high mean airway pressure or inadequate exhalation time resulting in overdistention or from such circulatory problems as.
However EtCO2 is not ready for primetime in sepsis. Conversely if the patient has low CO 2 perhaps because of hyperventilation it will cause an increased affinity for oxygen allowing hemoglobin to pick oxygen up more easily. Shortness of breath from anxiety-induced hyperventilation is caused by an excess of CO2 exhalation.
However utilizing end-tidal capnography in the evaluation of diabetic patients with suspected DKA is a quick and noninvasive method both to approximate the presence and. Monitoring of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 is a noninvasive method that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2. What Does Low End Tidal Co2 Mean.
This non-invasive monitor can give valuable information about cardiac output perfusion and ventilation. In critical care End Tidal CO2 monitoring is used to assess adequacy of circulation to the lungs which provides clues about circulation to the rest of the body. Low EtCO2 with other signs of shock indicates poor systemic perfusion which can be caused by hypovolemia sepsis or dysrhythmias.
30 patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery under General Anaesthesia were ventilated with tidal volume. With pulmonary embolism a blocked pulmonary artery causes less CO2-rich blood to return to the lungs and less CO2 is released with each breath. This is going to increase the elimination of CO2.
It monitors the partial pressure of carbon dioxide CO 2 in respiratory gases. When the ventilator runs with a normal rate but the minute volume is too high Who are in shock With normal respiratory rate and tidal volume but with a low body temperature Can also be seen in patients with spontaneous respiration when they are compensating a metabolic acidosis. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of low tidal volume ventilation on acid base status during pneumoperitonium.
When ETCO2 is low with other signs of shock it indicates poor systemic perfusion which can be caused by hypovolemia sepsis or dysrhythmias. Utilizing End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide to Diagnose Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Prehospital Patients with Hyperglycemia Prehosp Disaster Med. Continuous Waveform Capnograpy is written as PETCO2 which stands for patient end-tidal carbon dioxide.
So our PaCO2 ends up being determined by the balance between CO2 production increased by acidosis and CO2 elimination increased by hyperventilation. 35-40 mm Hg PETCO2 less than 10 indicates ineffective chest compressions. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring ETCO2 has clinical uses far beyond solely determining hypo- or hyperventilation.
ETCO2 is a reliable indicator with a high prognostic value in determining the CPR outcome 11 12. In normal conditions CO2 is 5 to 6 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. Dead-space ventilation results in ventilated alveoli with insufficient perfusion which leads to low ETco 2.
However if the low. Capnography provides an indirect means to detect metabolic acidosis. Carbon dioxide is produced in the body as a by-product of metabolism and is eliminated by exhaling.
Other respiratory conditions can cause a low ETCO2 reading or hypocapnea. What is the normal range for end tidal CO2. After 20 minutes of CPR death occurs if ETCO2 is consistently below 10 mmHg with 100 sensitivity and specificity 15.
But in a patient with intact respiratory drive theyre going to respond to the acidosis by increasing their tidal volume and respiratory rate. Studies have shown that in patients who had ETCO2 of 10 mmHg or less cardiac arrest was associated with death 13 14. Previous studies have shown that low EtCO 2 levels correlate with elevated lactate levels and predict mortality in patients with suspected sepsis.
Levels less than 35 mm Hg correlate with lactate 4 mmolL 29 while levels less than 31 mm Hg correlate with higher mortality 3132. Definition of Low CO2 hypocapnia Hypocapnia hypocapnea also known as hypocarbia is defined as a deficiency of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood. The partial pressure of CO 2 at end expiration is termed end tidal CO 2 ETCO 2.
What Is A Normal End Tidal Co2. While we disagree in giving a bicarb drip as mentioned in the video it does demonstrate the acid-base physiology in real time. End-tidal clearance must be evaluated in the context of the patients perfusion status.
As lactate and acidosis worsen EtCO2 decreases. This is a major respiratory symptom. End-tidal capnography has gained momentum over the years as a standard for monitoring patients undergoing procedural sedation in the emergency department with a level B recommendation coming out of ACEPs clinical policy regarding procedural sedation in 2014.
There is no current consensus regarding which EtCO2 levels can be used consistently in practice to rule in or rule out metabolic acidosis and therefore DKA in the right clinical setting. Acid base alterations occur during laparoscopy with carbon dioxide insufflation. Furthermore out-of-hospital ETCO2 was significantly correlated with measures of metabolic acidosis.
Lets face it your clinical assessment and gestalt still remain at the top for these patients. Most medical sources define hypocapnia as less than 35 mm Hg for partial CO2 pressure in the arterial blood. Can be observed in artificially ventilated patients.
There is a large volume of data suggesting that failure to achieve an end-tidal CO2 above 10 mmHg within the first 20 minutes of CPR is. The effect of administration of Sodium bic arbonate on the end-tidal CO2 in an intubated patient with severe metabolic acidosis is well demonstrated by this video by Dr.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
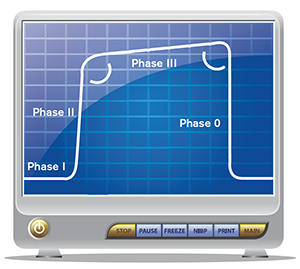
End Tidal Capnography Can Be Useful For Detecting Diabetic Ketoacidosis Monitoring Copd Acep Now

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

End Tidal Co2 Emergency Medicine Icu Nursing Paramedic School
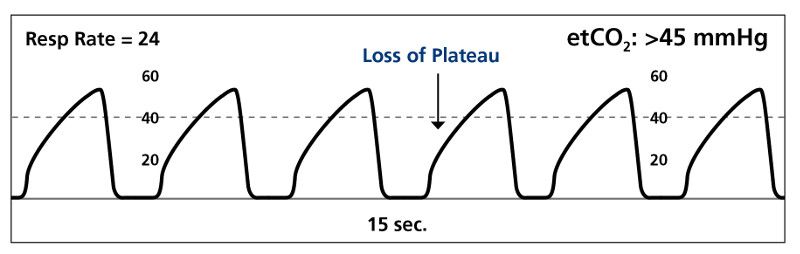
5 Medical Conditions Where Capnography Can Affect Bls Care

End Tidal Capnography Can Be Useful For Detecting Diabetic Ketoacidosis Monitoring Copd Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

Pv Card Continuous End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In Cardiac Arrest Cardiac Nursing Cardiac Arrest Medical Knowledge

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Pdf Applications Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Monitoring In Emergency Department A Narrative Review Semantic Scholar